Selecting an LMS requires learning and development leaders to evaluate platforms across content support, integrations, compliance features, analytics, administration complexity, scalability, and learner experience. Because LMS platforms serve diverse use cases, selection decisions must align with organizational training strategy and workforce composition.
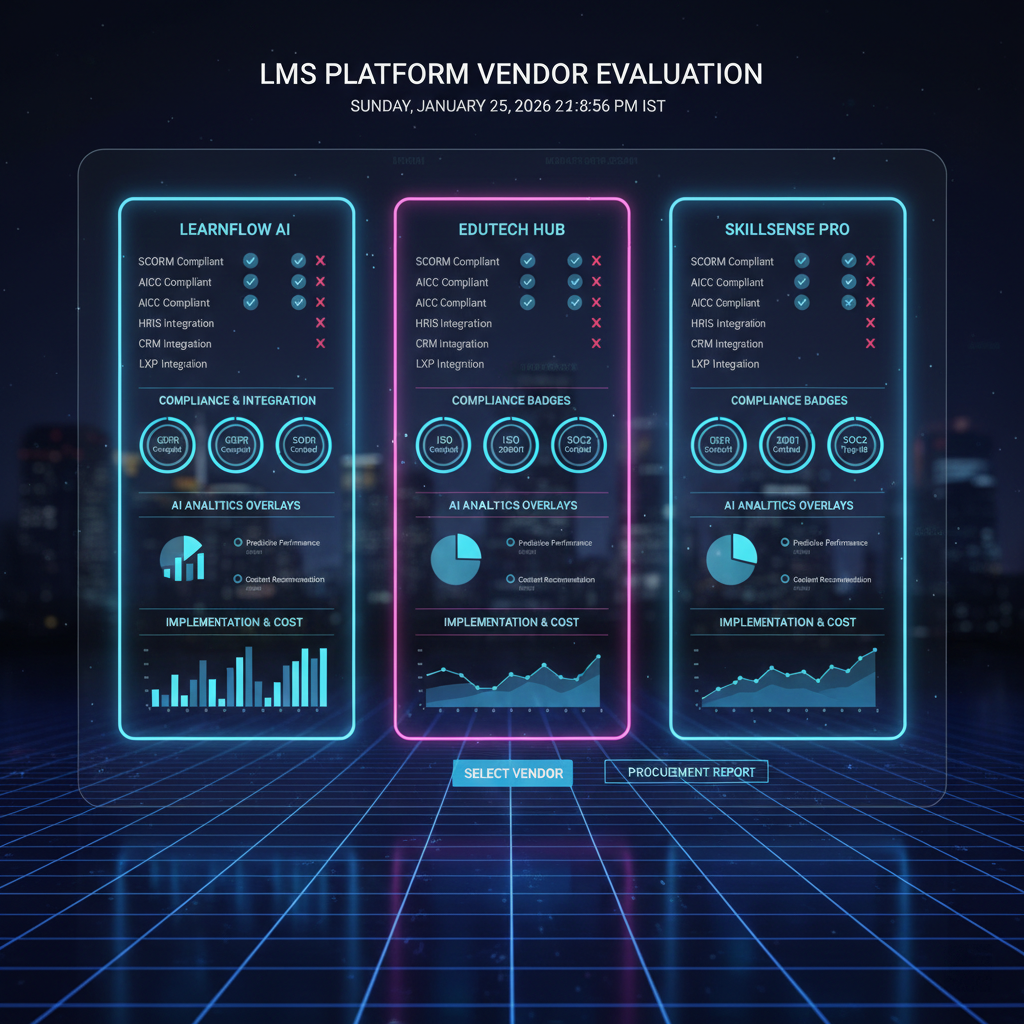
Content compatibility determines whether the LMS supports SCORM, xAPI, video, interactive modules, and mobile learning formats. Organizations using external content libraries or in-house authoring tools must ensure compatibility to prevent lock-in or rework.
Integration capabilities influence ecosystem fit. LMS platforms must connect to HRIS systems for provisioning, to performance management systems for skill evaluation, and to content providers for learning expansion. API availability and pre-built connectors accelerate deployment.
Compliance management features are crucial for regulated industries. LMS must support certification tracking, automated reminders, audit logs, and role-based assignment. Organizations must validate compliance standards during procurement.
Analytics and reporting differentiate mature solutions. Leaders should evaluate dashboards for learner performance, completion, assessment scores, and compliance status. Executive reporting supports ROI justification and strategic planning.
Learner experience influences adoption. Modern LMS platforms must provide intuitive navigation, mobile compatibility, microlearning support, and role-based learning paths. Poor UX reduces engagement and training effectiveness.
Scalability matters for enterprise deployments spanning global workforces, subsidiaries, and distributed teams. Multi-language support, multi-region hosting, and multi-business-unit configuration are important for multinational organizations.
By applying structured evaluation criteria, organizations can select an LMS that aligns learning delivery with workforce strategy and operational outcomes.